Scapy: تفاوت میان نسخهها
بدون خلاصۀ ویرایش |
|||
| (۸ نسخهٔ میانی ویرایش شده توسط ۵ کاربر نشان داده نشد) | |||
| خط ۶: | خط ۶: | ||
== ساختار یک بسته == | == ساختار یک بسته == | ||
در شکل زیر ساختار لایه بندی یک بسته | در شکل زیر ساختار لایه بندی یک بسته شبکه از نوع icmp نشان داده شده است. | ||
[[پرونده:Pkt-layers.png|ساختار بسته در شبکه]] | [[پرونده:Pkt-layers.png|ساختار بسته در شبکه]] | ||
| خط ۷۸: | خط ۷۸: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
لیست این | لیست این پروتکل ها بصورت زیر است: | ||
<div dir="ltr"> | <div dir="ltr"> | ||
< | |||
<nowiki> | |||
version : BitField = (4) | version : BitField = (4) | ||
ihl : BitField = (None) | ihl : BitField = (None) | ||
| خط ۹۵: | خط ۹۷: | ||
dst : Emph = ('127.0.0.1') | dst : Emph = ('127.0.0.1') | ||
options : PacketListField = ([]) | options : PacketListField = ([]) | ||
</nowiki> | </nowiki> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| خط ۱۶۳: | خط ۱۶۶: | ||
== مراجع == | == مراجع == | ||
* [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-01-scapy-introduction-and-overview/ مروری بر قابلیت های اسکپی] | * [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-01-scapy-introduction-and-overview/ مروری بر قابلیت های اسکپی] | ||
* [https://thepacketgeek.com/series/building-network-tools-with-scapy/#ping-sweep آموزش تکمیلی اسکپی] | |||
* [http://thepacketgeek.com/series/building-network-tools-with-scapy/ نصب پایتون و اسکپی] | * [http://thepacketgeek.com/series/building-network-tools-with-scapy/ نصب پایتون و اسکپی] | ||
* [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-03-scapy-interactive-mode/ کار با اسکپی در حالت تعاملی] | * [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-03-scapy-interactive-mode/ کار با اسکپی در حالت تعاملی] | ||
| خط ۱۶۹: | خط ۱۷۳: | ||
* [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-06-sending-and-receiving-with-scapy/ ارسال و دریافت بسته با اسکپی] | * [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-06-sending-and-receiving-with-scapy/ ارسال و دریافت بسته با اسکپی] | ||
* [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-07-monitoring-arp/ مشاهده بسته های ARP] | * [http://thepacketgeek.com/scapy-p-07-monitoring-arp/ مشاهده بسته های ARP] | ||
* http://www.secdev.org/projects/scapy/ | |||
* http://www.secdev.org/projects/scapy/doc/usage.html | |||
* http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/request-response.html | |||
* http://www.scmdt.mmu.ac.uk/blossom/downloads/byDoing/PythonScriptingwithScapyLab.pdf | |||
* [http://packetlife.net/media/library/36/scapy.pdf Visiopscapy] | |||
* [http://www.secdev.org/conf/scapy_hack.lu.pdf Presentation] | |||
* [https://coderwall.com/p/2es5jw/docker-cheat-sheet-with-examples Docker Cheat Sheet with examples ] | |||
* [http://www.secdev.org/projects/scapy/build_your_own_tools.html ساخت چند ابزار کاربردی شبکه: پینگ، مانیتورینگ] | |||
* [http://bt3gl.github.io/black-hat-python-infinite-possibilities-with-the-scapy-module.html Black Hat Python: Infinite possibilities with the Scapy Module] | |||
* [Investigating a tricky network problem with Python, Scapy and other network tools http://cybergibbons.com/reverse-engineering-2/investigating-a-tricky-network-problem-with-python-scapy-and-other-network-tools/] | |||
* | |||
نسخهٔ کنونی تا ۱۹ فوریهٔ ۲۰۱۶، ساعت ۰۱:۱۷
اسکپی (Scapy) ابزاری متن باز و تحت زبان برنامه نویسی پایتون است که به کمک آن میتوان فعالیت هایی را در زمینه کار با بسته (Packet) های موجود در شبکه های کامپیوتری نظیر ایجاد بسته ، مشاهده و ثبت بسته های شبکه، تغییر و ارسال بسته ها در شبکه را انجام داد.
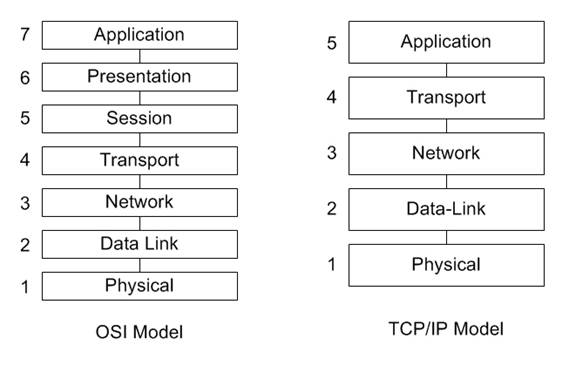
آشنایی با لایه های شبکه برای کار با این ابزار ضروری است. مدل های لایه ای شبکه در تصویر مقابل نشان داده شده است. برای اطلاعات بیشتر میتوانید به [۱] یا [۲] مراجعه نمایید.
ساختار یک بسته
در شکل زیر ساختار لایه بندی یک بسته شبکه از نوع icmp نشان داده شده است.
شروع کار با اسکپی
برای مشاهده لیست دستورات اسکپی در حالت تعاملی دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
lsc()
لیست این دستورات بصورت زیر است:
>>> lsc() arpcachepoison : Poison target's cache with (your MAC,victim's IP) couple arping : Send ARP who-has requests to determine which hosts are up bind_layers : Bind 2 layers on some specific fields' values corrupt_bits : Flip a given percentage or number of bits from a string corrupt_bytes : Corrupt a given percentage or number of bytes from a string defrag : defrag(plist) -> ([not fragmented], [defragmented], defragment : defrag(plist) -> plist defragmented as much as possible dyndns_add : Send a DNS add message to a nameserver for "name" to have a new "rdata" dyndns_del : Send a DNS delete message to a nameserver for "name" etherleak : Exploit Etherleak flaw fragment : Fragment a big IP datagram fuzz : Transform a layer into a fuzzy layer by replacing some default values by random objects getmacbyip : Return MAC address corresponding to a given IP address hexdiff : Show differences between 2 binary strings hexdump : -- hexedit : -- is_promisc : Try to guess if target is in Promisc mode. The target is provided by its ip. linehexdump : -- ls : List available layers, or infos on a given layer promiscping : Send ARP who-has requests to determine which hosts are in promiscuous mode rdpcap : Read a pcap file and return a packet list send : Send packets at layer 3 sendp : Send packets at layer 2 sendpfast : Send packets at layer 2 using tcpreplay for performance sniff : Sniff packets split_layers : Split 2 layers previously bound sr : Send and receive packets at layer 3 sr1 : Send packets at layer 3 and return only the first answer srbt : send and receive using a bluetooth socket srbt1 : send and receive 1 packet using a bluetooth socket srflood : Flood and receive packets at layer 3 srloop : Send a packet at layer 3 in loop and print the answer each time srp : Send and receive packets at layer 2 srp1 : Send and receive packets at layer 2 and return only the first answer srpflood : Flood and receive packets at layer 2 srploop : Send a packet at layer 2 in loop and print the answer each time traceroute : Instant TCP traceroute tshark : Sniff packets and print them calling pkt.show(), a bit like text wireshark wireshark : Run wireshark on a list of packets wrpcap : Write a list of packets to a pcap file
برای مشاهده لیست پروتکل هایی که در اسکپی پشتیبانی می شود دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
ls()
همچنین می توانید لیست پروتکل ها را به تفکیک لایه مورد نظر مشاهده نمایید که دستور زیر را برای نمونه وارد کنید:
ls(IP)
لیست این پروتکل ها بصورت زیر است:
version : BitField = (4)
ihl : BitField = (None)
tos : XByteField = (0)
len : ShortField = (None)
id : ShortField = (1)
flags : FlagsField = (0)
frag : BitField = (0)
ttl : ByteField = (64)
proto : ByteEnumField = (0)
chksum : XShortField = (None)
src : Emph = (None)
dst : Emph = ('127.0.0.1')
options : PacketListField = ([])
برای شروع، جهت دریافت یک نمونه بسته از روی کارت شبکه دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
pkts = sniff(count=100)
برای مشاهده پیش نمایشی از بسته های دریافت شده، دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
pkts.show()
یا
print pkts
یا
hexdump(pkts)
برای مشاهده آمار بسته های دریافت شده از نظر پروتکلی دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
pkts.summary
یا
pkts
کار با یک بسته
برای مشاهده یک بسته، میتوانید اندیس یا شماره بسته مورد نظر را بصورت زیر وارد کنید:
pkts[10]
یا نمایش بصورت هگز
hexdump(pkts[10])
یا نمایش بصورت اسکی
print pkts[10]
برای مشاهده اطلاعات خلاصه ای درباره یک بسته، دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
pkts[10].summary()
برای مشاهده ساختار کامل یک بسته بصورت سلسله مراتبی دستور زیر را وارد کنید:
pkts[10].show()
مراجع
- مروری بر قابلیت های اسکپی
- آموزش تکمیلی اسکپی
- نصب پایتون و اسکپی
- کار با اسکپی در حالت تعاملی
- مشاهده داخل یک بسته
- ارسال یک بسته نمونه (بسته ARP)
- ارسال و دریافت بسته با اسکپی
- مشاهده بسته های ARP
- http://www.secdev.org/projects/scapy/
- http://www.secdev.org/projects/scapy/doc/usage.html
- http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/request-response.html
- http://www.scmdt.mmu.ac.uk/blossom/downloads/byDoing/PythonScriptingwithScapyLab.pdf
- Visiopscapy
- Presentation
- Docker Cheat Sheet with examples
- ساخت چند ابزار کاربردی شبکه: پینگ، مانیتورینگ
- Black Hat Python: Infinite possibilities with the Scapy Module
- [Investigating a tricky network problem with Python, Scapy and other network tools http://cybergibbons.com/reverse-engineering-2/investigating-a-tricky-network-problem-with-python-scapy-and-other-network-tools/]